The figure is calculated at the end of each accounting period (monthly, quarterly, or annually). As the formula suggests, retained earnings are dependent on the corresponding figure of the previous term. The resultant number may be either positive or negative, depending on the net income or loss generated by the company over time. Alternatively, the company paying large dividends that exceed the other figures can also lead to the retained earnings going negative.
Financial Accounting
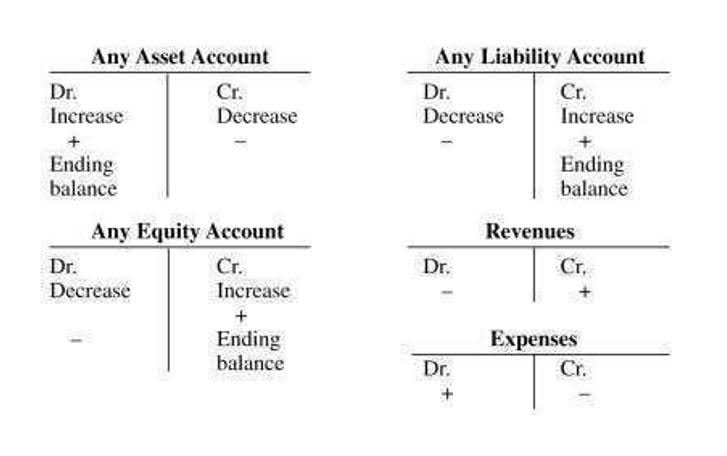
- With this system, every transaction has at least two entries made for it with one being debit and another being credit.
- Thus, they do not have sufficient patronage to ensure their profitability yet.
- Conversely, for liability and equity accounts, a credit increases the balance, and a debit decreases it.
- This statement reconciles the beginning and ending balances of retained earnings for a specific accounting period.
- When the year’s revenues and gains exceed the expenses and losses, the corporation will have a positive net income which causes the balance in the Retained Earnings account to increase.
- Conversely, if a company incurs a net loss, this loss reduces the accumulated earnings, and it is recorded as a debit to retained earnings, thereby decreasing the balance.
For reference, the chart below sets out the type, side of the accounting equation (AE), and the normal balance of some typical accounts found within a small business bookkeeping system. For example, company B made an error in the 2019 financial statements by not recording an amortization expense of one of the intangible assets. Retained AI in Accounting earnings are not cash; they represent profits that may be tied up in assets such as inventory, equipment, or accounts receivable. Now, let’s say ABC Corporation declares and pays dividends of $10,000 to its shareholders during the year. Dividends decrease the balance in the Retained Earnings account, so we would debit the Retained Earnings account by $10,000.
Retained earnings on the balance sheet
When a company pays dividends to its shareholders, it reduces its retained earnings by the amount of dividends paid. A statement of retained earnings details the changes in a company’s retained earnings balance over a specific period, usually a year. As a form of shareholders’ equity, retained earnings are a valuable measurement of your business’s health. You can find retained earnings under the category of shareholder’s equity on your balance sheet.

Does Retained Earnings Increase With Debit or Credit?
Since retained earnings represent a portion of the owner’s equity, an increase in these accumulated profits is recorded as a credit, aligning with the normal balance convention for equity accounts. Retained earnings are usually recorded on the right column of a company’s balance sheet under the equity section along with the company’s share capital and paid-in capital. Businesses are generally run with the hope of generating profits from the goods and services provided. During the business lifetime, the company generates profit and accumulated them in the retained earnings under equity section. At the end of accounting period, the income statement needs to be reset to zero.
Add Your Net Income (or Net Loss) from the Current Period
When dividends are declared, the company commits to paying out a portion of its accumulated earnings, which results in a debit to the retained earnings account, thereby lowering its balance. Conversely, a net loss incurred by a company will decrease retained earnings. A net loss occurs when expenses exceed revenues, effectively reducing the accumulated profits available within the business.
What Does On Account Mean in a Journal Entry?
Thus, the retained earnings are credited to the Retained Earnings Account. A net loss would decrease retained earnings so we would do the opposite in this journal entry by debiting Retained Earnings and crediting Income Summary. While not cash itself, a strong retained earnings balance indicates that a company has generated profits historically and possesses resources for future investments or managing liabilities. Lenders often view the level of retained earnings as an indicator of financial stability when assessing creditworthiness. These examples demonstrate the various ways retained earnings are impacted by business activities, including the distribution of dividends, correction of errors, and end-of-period closing entries. Retained earnings play a crucial role in reflecting the cumulative earnings and losses of a company over time.
- Retained earnings appear on the trial balance as part of equity and represent the link between the income statement and the balance sheet.
- Retained earnings, on the other hand, specifically refer to the portion of a company’s profits that remain within the business instead of being distributed to shareholders as dividends.
- The resulting figure is the ending retained earnings balance, which carries over to the current balance sheet.
- The “normal balance” of an account refers to the side of the T-account (debit or credit) where increases to that specific account are recorded.
- A net loss occurs when expenses exceed revenues, effectively reducing the accumulated profits available within the business.
The company accumulated profit will include in the accumulated retained earnings on balance sheet. When the company process the distribution to the owner, they will reduce the company cash balance as it is made in form of cash. Net loss willbe debited to Retained Earnings account thus results to a debitbalance. Retained Earnings with a debit balance will be called as’Deficits” or “Accumulated Deficits”. They are a measure of a company’s financial health, and they can promote stability and growth. Retained earnings are the portion of a company’s cumulative profit that is held or retained and saved for future use.
Retained Earnings Normal Balance and Its Changes
- Owner distribution is the allocation of the company retained earnings to the owners.
- This ensures financial statements accurately reflect performance for the specific period and the balance sheet carries the correct cumulative equity figure forward.
- This indicates its role as a component of the owners’ claim on company assets, alongside other equity elements like common stock.
- Hence, retained earnings are the portion of a company’s net income that is set aside by the company for various operational purposes after dividend payments to its shareholders.
- Corporations retain earnings as a way to reinvest in the business or to save for future expenses, acquisitions, or debt repayment.
- Conversely, when a company distributes profits to shareholders as dividends, this action reduces the owners’ claim on the company’s assets.
Retained earnings are one of the options available to a company’s shareholders when distributing profits at the end of an accounting period. Although each account has a normal balance in practice it is possible for any account to have either a debit or a credit balance depending on the bookkeeping entries made. So for example there are contra expense accounts such as purchase returns, contra revenue accounts such as sales returns and contra asset accounts such as accumulated depreciation. Stay on top of your finances with real-time access to your general ledger, balance sheet, profit and loss, and cash flow statements. Kpi.com offers monthly, quarterly, or annual management financial reports produced to local and international financial reporting standards. When companies keep a record of their transactions, they do so using the double-entry bookkeeping system.

Subtract Cash Dividends and Stock Dividends
This consistent application of debit and credit rules ensures the accounting equation remains balanced and accurately reflects changes in a company’s financial position. These principles are part of Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP), which guide financial reporting in the United States. It is a cumulative balance, meaning it carries forward from one accounting period to the next, reflecting does retained earnings have a debit or credit balance all past earnings and distributions.
What are Retained Earnings? And How do companies use them to balance growth and dividend distribution?
Some factors https://www.azurmavitransfer.com/semi-monthly-vs-biweekly-payments/ that can affect a company’s retained earnings include depreciation, COGS, dividends, etc. Beyond the balance sheet, retained earnings are also detailed in the Statement of Retained Earnings, sometimes called a Statement of Changes in Equity. This statement reconciles the beginning and ending balances of retained earnings for a specific accounting period. It illustrates how net income increases retained earnings and how dividends paid decrease it, ultimately showing the ending balance that flows directly to the balance sheet. Retained earnings represents the portion of a company’s net income that is reinvested in the business rather than distributed to shareholders as dividends. It accumulates over time and can be used for expansion, debt repayment, research and development, or other corporate needs.




